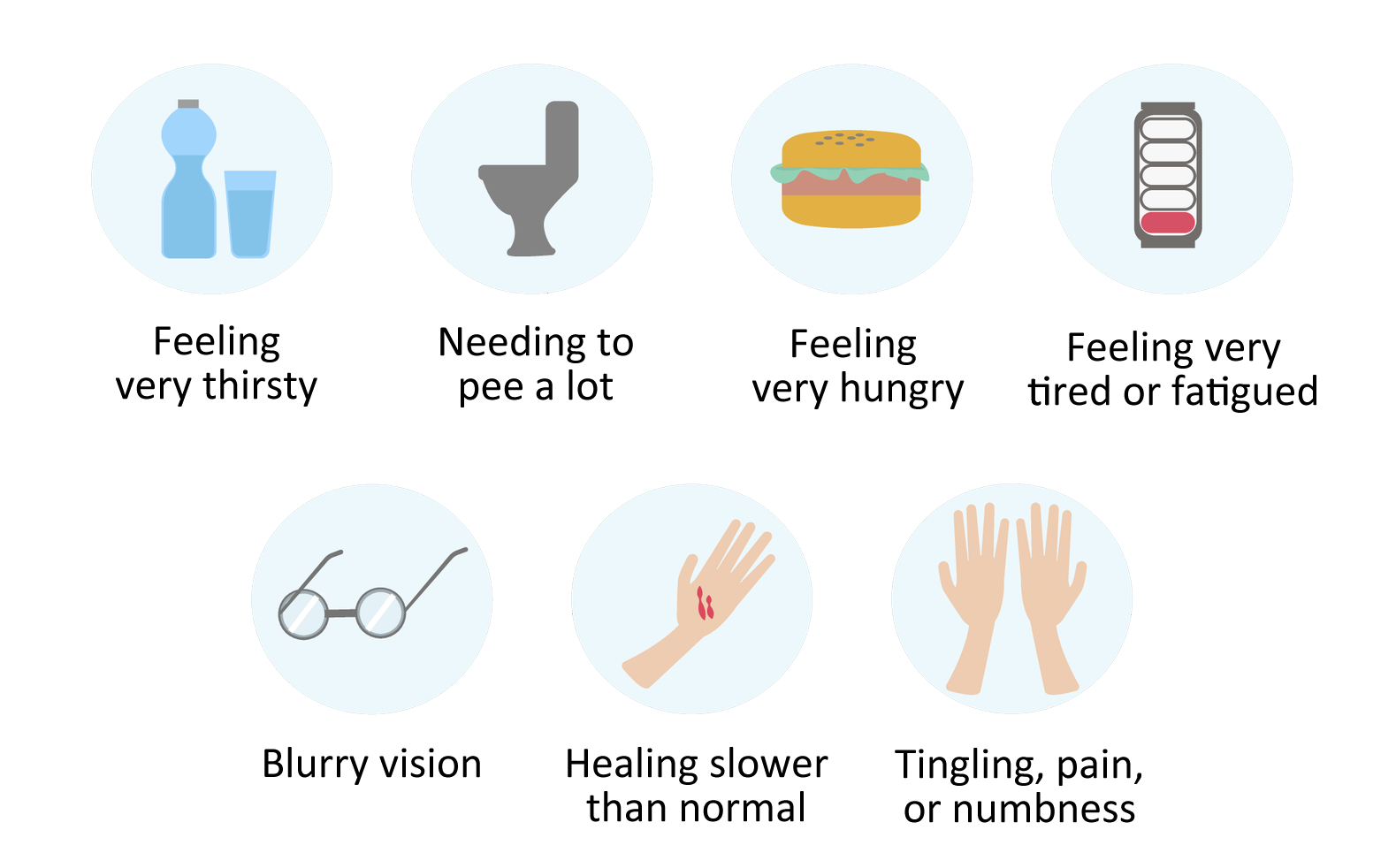
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and pancreatic endocrine dysfunction.1 Those with T2DM can experience a variety of symptoms, mostly related to hyper- and hypoglycemia and complications associated with diabetes. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) lists seven common symptoms of T2DM on their website: frequent urination; excessive thirst; excessive hunger despite eating normally; extreme fatigue; blurry vision; cuts or bruises that are slow to heal; and tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands or feet.2
A 1994 study developed the Type 2 Diabetes Symptom Checklist (DSC-2) as a standardized tool for assessing both physical and psychological symptoms associated with T2DM in clinical and epidemiological research.3 The checklist was developed through a comprehensive literature review, using subject area expert consultations, and by surveying patients with T2DM, who were asked to rank symptoms based on their frequency and perceived burden. Since then, it has been updated to the Diabetes Symptoms Checklist-Revised (DSC-R).4 The DSC-R includes 34 diabetes-related symptoms, as outlined below.
Table 1. Type 2 Diabetes Symptom Checklist-Revised (DSC-R)
|
Dimensions
|
Symptoms
|
|
Hyperglycemia
|
Very thirsty
Dry mouth
Drinking a lot (all sorts of drinks)
Frequent voiding
|
|
Hypoglycemia
|
Easily irritated or annoyed
Irritability just before a meal
Moodiness
|
|
Psychological - Fatigue
|
Lack of energy
Overall sense of fatigue
Fatigue in the morning when getting up
Increasing fatigue in the course of the day
|
|
Psychological - Cognition
|
Sleepiness or drowsiness
Difficulty concentrating
Difficulty staying attentive
Dull head
|
|
Cardiac
|
Shortness of breath during exercise
Shortness of breath at night
Palpitations
Pains in the breast or heart region
|
|
Neuropathy - Pain
|
Aching calves when walking
Shooting pains in the legs
Burning pain in the calves at night
Burning pain in the legs during the day
|
|
Neuropathy - Sensation
|
Numbness (loss of sensation) in the hands
Numbness (loss of sensation) in the feet
Tingling or prickling in the hands or fingers
Tingling or prickling in the legs or feet
Odd feeling in the legs or feet when touching
Tingling in the limbs at night
|
|
Vision
|
Persistently blurred vision (also with glasses)
Deteriorating vision
Flashes or black spots in the field of vision
Fluctuating clear and blurred vision
Sudden deterioration in vision
|
A 2005 study (n=1137) analyzed the symptoms, signs, and complications in patients newly diagnosed with T2DM and their relationship with blood glucose levels, blood pressure, and weight.5 It found that 89% exhibited at least one symptom at diagnosis, with the most common being abnormal thirst (63.7%), frequent urination (53.9%), fatigue (61.0%), unintended weight loss (34.8%), and visual disturbances (24.9%).w These symptoms were strongly associated with rising blood glucose levels, although their pre-diagnostic duration was less than three months. In contrast, cardiovascular complications such as angina pectoris and intermittent claudication often had a longer pre-diagnostic duration, sometimes exceeding one to two years. Other symptoms including genital itching, stomatitis, and balanitis also showed significant correlation with elevated glycemic levels. There was little association between diabetes symptoms and blood pressure or obesity, suggesting that glycemic level was the primary driver of diabetes symptoms rather than other metabolic risk factors. These findings highlight the importance of recognizing early symptoms for timely diagnosis, as most patients sought medical attention due to these signs.
A study published in 2007 examined the prevalence of seven symptoms among 3,937 participants with T2DM.6 Excessive thirst had the strongest association (20% prevalence, Odds Ratio [OR] 2.48, p<0.001), followed by unusual weight loss (4.4%, OR 1.68, p<0.001), blurry vision (18.2%, OR 1.58, p<0.001), frequent urination (33.8%, OR 1.28, p<0.001), increased fatigue (27.3%, OR 1.19, p=0.002), and extreme hunger (9.5%, OR 1.55, p<0.001). However, 44% of participants reported experiencing none of these symptoms. This emphasizes the need for proactive screening and the importance of routine blood glucose testing, especially for individuals at high risk.
Although signs and symptoms can be helpful in identifying patients who may have T2DM, the criteria for diagnosis include serum glucose testing. According to the ADA, a positive diagnosis of T2DM requires one of the following:7
- A1C ≥6.5% (≥48 mmol/mol)
- Fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL (≥7.0 mmol/L)
- 2-hour plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL (≥11.1 mmol/L) during a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test
- Random plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL (≥11.1 mmol/L) in an individual with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis
References
- 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. Jan 1 2022;45(Suppl 1):S17-s38. doi:10.2337/dc22-S002
- Association AD. Understanding Type 2 Diabetes. Accessed March 18, 2025. https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/type-2
- Grootenhuis P, Snoek F, Heine R, Bouter L. Development of a type 2 diabetes symptom checklist: a measure of symptom severity. Diabetic Medicine. 1994;11(3):253-261.
- Arbuckle RA, Humphrey L, Vardeva K, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Diabetes Symptom Checklist-Revised (DSC-R)--a measure of symptom distress. Value Health. Nov-Dec 2009;12(8):1168-75. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00571.x
- Drivsholm T, de Fine Olivarius N, Nielsen AB, Siersma V. Symptoms, signs and complications in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients, and their relationship to glycaemia, blood pressure and weight. Diabetologia. Feb 2005;48(2):210-4. doi:10.1007/s00125-004-1625-y
- Clark NG, Fox KM, Grandy S, Group SS. Symptoms of diabetes and their association with the risk and presence of diabetes: findings from the Study to Help Improve Early evaluation and management of risk factors Leading to Diabetes (SHIELD). Diabetes Care. Nov 2007;30(11):2868-73. doi:10.2337/dc07-0816
- 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. Jan 1 2025;48(Supplement_1):S27-s49. doi:10.2337/dc25-S002